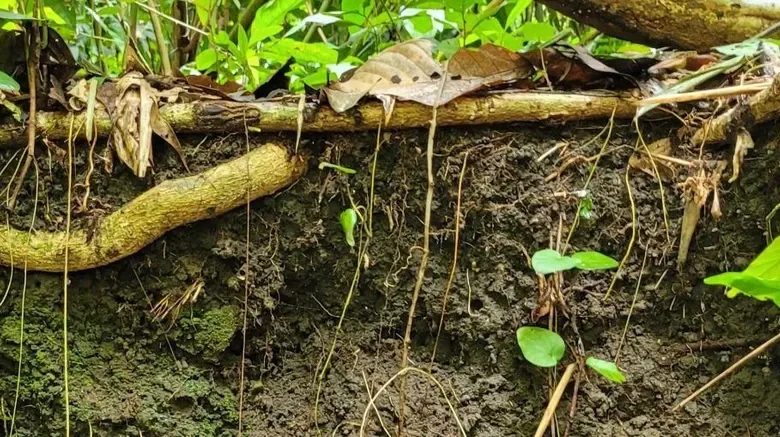
Soil is formed through a process called weathering, which involves the breaking down of rocks and minerals by physical, chemical, and biological agents. During weathering, rocks are broken into smaller particles, and organic materials such as leaves and dead organisms are added to the mix.
Over time, these particles and organic materials accumulate, creating a layer of soil. This process can take thousands or even millions of years, depending on the conditions. Soil, the foundation of terrestrial life, plays a crucial role in supporting plant growth, regulating water resources, and serving as a habitat for countless organisms.
But have you ever wondered how soil is formed? To grasp this phenomenon, we delve into the captivating forces of weathering, which gradually transforms solid rocks into the precious ground we walk upon.
As weathering processes cause rocks to crumble, various agents like physical, chemical, and biological factors assist in breaking them down into smaller particles. This intricate dance between nature and time results in the accumulation of sediment and organic matter, creating the diverse and valuable soils that sustain our ecosystems. Let’s unravel the fascinating journey of soil formation.
Unveiling The Earth’s Secret Recipe
Welcome to our exploration of the hidden alchemy that shapes the very ground we stand on. As we delve into the captivating science behind soil formation, we unravel the Earth’s secret recipe for creating this essential ingredient for life. Join us as we embark on a journey to understand the fascinating forces and factors that contribute to the genesis of soil.
The Foundation Of Soil
Soil formation is a captivating process that evolves over centuries, sculpted by a meticulous blend of geological, biological, and chemical interactions. Weathering of rocks and minerals, biological activities of organisms, and the influence of climate all contribute to the intricate tapestry of soil composition.
This complex interplay begins with the disintegration of rocks through physical and chemical processes, leading to the birth of mineral particles. As organic matter accumulates and mixes with these particles, the soil gains fertility, structure, and vitality. The components present in the parent material, along with the organic materials contributed by plants and animals, form the fundamental building blocks of soil.
The Role Of Climate And Weather
Climate and weather act as master sculptors, shaping and molding the formation of soil. The intensity of rainfall, temperature fluctuations, and the erosive force of wind all leave their indelible mark on the soil. Precipitation and temperature variations instigate processes such as leaching, erosion, and deposition, all of which play pivotal roles in the ongoing transformation of the Earth’s surface into fertile ground.
The interplay between climate, geology, and biological activity determines the type and quality of the soil that emerges. The collective influence of these elements engenders a diverse spectrum of soil types, each bearing the imprint of the unique environmental conditions to which they have been subjected over time.

Credit: www.amazon.com
Agents Of Transformation
Soil is formed through the gradual process of rock weathering, organic matter decomposition, and microbial activity. Water and plant roots play key roles in breaking down rocks and organic material, creating fertile soil for growth and sustainability. This natural transformation highlights the intricate relationship between land and life.
Agents of Transformation play a crucial role in the formation of soil. These agents include Biological Activity and Physical Processes. Let’s explore how these factors contribute to the transformation of raw materials into the rich, fertile soil that sustains life.
Biological Activity
Biological Activity refers to the action and impact of microorganisms, plants, and animals on the soil formation process. The activities of these organisms result in the decomposition of organic matter, nutrient cycling, and the formation of soil aggregates. Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi break down organic matter, including dead plants and animals, into simpler forms. This decomposition process is an essential step in releasing nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plant uptake. The roots of plants also play a vital role in soil formation.
As plants grow, they excrete organic compounds and release carbon dioxide through their roots. This process, known as exudation, stimulates the development of a healthy microorganism community, which further enhances the decomposition of organic matter. Furthermore, plant roots physically bind the soil particles together, forming aggregates. These aggregates help create a stable soil structure, improving its ability to retain water and resist erosion.
Physical Processes
Physical Processes refer to the mechanical actions that shape the soil. These processes include weathering, erosion, transportation, and deposition. Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals into smaller particles. This can occur through physical processes such as freeze-thaw cycles, where water expands as it freezes, causing rocks to crack. Chemical processes, such as the action of acids, can also contribute to weathering.
Erosion happens when wind or water carries away soil particles from one place and deposits them elsewhere. It is a natural process that can be accelerated by human activities like deforestation or improper land use practices. Erosion can lead to the loss of topsoil, which is the most fertile layer of soil. Transportation involves the movement of soil particles by wind, water, or gravity. These agents carry particles over long distances, allowing for the redistribution of minerals and organic matter in the soil profile.
Deposition occurs when the transported soil particles settle and accumulate in a new location. This can happen in river deltas, floodplains, or areas where windblown sediments accumulate. formation and its importance in sustaining life.
Time: A Key Ingredient
The formation of soil takes place over thousands, millions, and even billions of years. It is through the passage of time that soil is gradually created via a remarkable process involving various factors. Understanding the impact of geological time on soil formation and the concept of soil formation rates provides valuable insights into the complexity and significance of this natural process.
Impact Of Geological Time
Geological time, stretching over vast periods, plays a crucial role in shaping the characteristics and composition of soil. The continuous interaction between different geological forces, weathering, erosion, and deposition significantly influence the formation and transformation of soil over time.
Weathering: Over time, the relentless forces of nature, such as wind, water, temperature, and ice, break down rocks into smaller particles. This process, known as weathering, gradually creates the mineral component of soil. The physical and chemical breakdown of rocks through weathering exposes new surfaces, enabling further weathering and contributing to the accumulation of organic matter.
Erosion: Erosion, another geological phenomenon, involves the movement and transportation of soil particles by wind, water, or ice. It acts as a driving force in redistributing the weathered materials and organic matter, eventually affecting soil formation. The duration and intensity of erosion events also influence the distribution of nutrients, organic matter, and minerals across different soil horizons.
Deposition: As erosion moves soil particles, the process of deposition occurs when these particles settle in new locations. Over time, these deposited particles mix with organic matter, minerals, microorganisms, and other components, contributing to the formation of new layers of soil.
The Concept Of Soil Formation Rates
Soil formation rates, which vary depending on environmental conditions and factors, provide insight into the timeframe required for significant changes to occur in soil properties. While soil formation is a gradual process, the rate at which it occurs can differ significantly.
Factors Affecting Soil Formation Rates:
- Climate: Climatic conditions, including temperature, precipitation, and moisture, directly impact the rate of soil formation. Fertile soils often develop in regions with moderate temperatures and ample rainfall, where increased weathering and organic matter accumulation prevail.
- Parent Material: The type and composition of the parent material from which soil is formed influence its formation rate. For instance, soil derived from volcanic rocks typically forms at a faster rate due to their mineral composition.
- Topography and Landscape: The shape, slope, and relief of the land affect soil formation rates. Steep slopes may experience higher erosion rates, leading to thinner and less developed soils.
- Biotic Factors: The presence of plants, microorganisms, animals, and their interactions with the environment influence the formation rates of soil. The organic matter derived from plants and the activities of soil organisms can accelerate or slow down soil formation.
The concept of soil formation rates highlights the intricate relationship between time, environmental conditions, and various factors involved in soil formation. Recognizing this relationship enables us to appreciate the incredible diversity and importance of soil across different ecosystems and landscapes.
Types Of Soil Composition
Soil composition plays a crucial role in its fertility and ability to support plant growth. Understanding the different components that make up soil can provide valuable insight into its characteristics and suitability for various purposes.
Mineral Composition
Mineral composition refers to the inorganic materials present in soil, including various minerals such as quartz, feldspar, and mica. These minerals originate from the weathering and breakdown of rocks over time, contributing to the physical and chemical properties of the soil. The proportion of different minerals can vary significantly, influencing factors such as drainage, texture, and nutrient availability.
Organic Matter Content
Organic matter content encompasses the decaying plant and animal remains, as well as microorganisms, that contribute to the fertility and structure of the soil. This organic material plays a vital role in nutrient cycling and soil aggregation, helping to improve water retention and overall soil health. The presence of organic matter is directly linked to the soil’s ability to support diverse and thriving ecosystems.
Human Influence On Soil Creation
Humans have a significant impact on the creation and composition of soil. Our activities, such as agricultural practices and urban development, play a crucial role in shaping the soil around us.
Agricultural Practices
Agricultural practices can either enhance or degrade the quality of soil. Through the use of fertilizers and pesticides, farmers affect soil fertility and structure. Over-reliance on chemicals can lead to soil erosion and compaction.
Urban Development
Urban development alters natural soil composition. Construction activities disrupt the soil structure, leading to compaction and reduced water infiltration. Urbanization also increases pollution levels in the soil from various sources.

Credit: www.snexplores.org
Conclusion
Understanding how soil is formed is crucial for sustainable agriculture and environmental conservation. By learning about the intricate processes that shape soil, we can better appreciate its significance in maintaining ecosystems and supporting life. With this knowledge, we can work towards protecting and improving soil health for future generations to thrive.