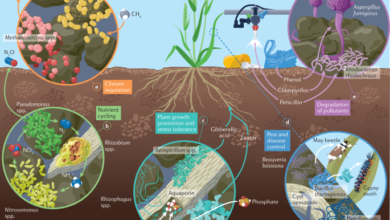
Compare the Use of Manure And Fertilizers in Maintaining Soil Fertility: Benefits Revealed
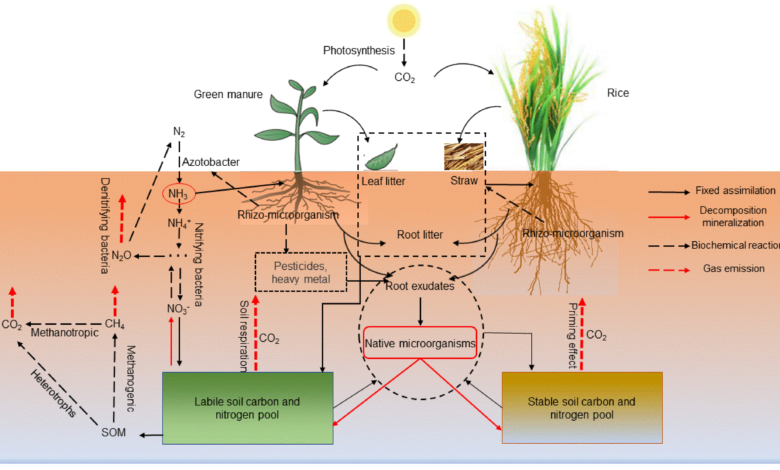
Manure and fertilizers are both used to maintain soil fertility, but they have different effects. Manure enriches the soil with organic matter and nutrients, increasing its fertility.
On the other hand, fertilizers are mostly inorganic compounds that can reduce soil fertility when used excessively, as they can be harmful to the symbiotic microorganisms in the soil. Fertilizers are considered to be beneficial for short-term use, while manure provides long-term benefits to the soil.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Comparison In Nutrient Content
In comparing nutrient content, manure enriches soil naturally with essential nutrients, while fertilizers can potentially reduce soil fertility over time due to their chemical composition. Manure provides organic matter and enhances soil health, while fertilizers, though providing immediate nutrients, may disrupt the soil’s natural balance and long-term fertility.
Organic Nutrients In Manure
In the quest for maintaining soil fertility, manure plays a crucial role. One of the main advantages of using manure is its ability to enrich the soil with organic nutrients. Manure is derived from animal excreta and plant waste, which undergo decomposition to create a nutrient-rich substance. Organic nutrients present in manure include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, along with other essential elements like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur.
Inorganic Nutrients In Fertilizers
On the other hand, synthetic fertilizers primarily consist of inorganic compounds. These fertilizers are created through chemical processes and provide readily available nutrients to the plants. The main inorganic nutrients found in fertilizers are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, commonly known as NPK. Additionally, fertilizers may also contain micronutrients like iron, manganese, and zinc, which are essential for plant growth and development.
When comparing the nutrient content of manure and fertilizers, both have their unique set of advantages. Manure provides a holistic approach by incorporating organic matter that improves soil structure and promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms. On the other hand, fertilizers offer precise control over nutrient supplementation, ensuring plants receive the necessary elements for optimal growth.
In summary, using manure for soil fertility offers the advantage of organic nutrients sourced from natural sources. However, its effectiveness may take time as it requires decomposition and gradual release of nutrients. Fertilizers, on the other hand, provide instant availability of nutrients but must be used with caution due to the potential negative impact on soil health. A balanced approach that combines both manure and fertilizers can be the key to achieving long-term soil fertility while maximizing plant growth.
Impact On Soil And Environment
Manure enriches soil nutrients without reducing fertility, while fertilizers, often inorganic, can diminish soil fertility with excessive use. Manure adds organic matter and nutrients through decomposition, benefiting soil microorganisms, whereas chemical fertilizers can harm the symbiotic organisms and should be used in moderation for short-term benefits.
Effects Of Manure On Soil Quality
Manure plays a crucial role in maintaining soil fertility and improving soil quality. When organic waste, such as animal excreta and plant matter, decompose, they produce manure. This natural fertilizer is rich in essential nutrients and organic matter, which benefits the soil in several ways.
Nutrient Enrichment: Manure enriches the soil by providing crucial nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for the healthy growth of plants and contribute to the overall fertility of the soil.
Organic Matter: One of the significant advantages of manure is its ability to increase the organic matter content in the soil. Organic matter improves the soil structure, promotes water retention, and enhances nutrient availability for plants. It also encourages the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the soil, which aid in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients.
Soil Retention and Drainage: Manure has a positive impact on both sandy and clayey soils. In sandy soils, it helps to retain water, preventing excessive drainage and ensuring the plants receive an adequate water supply. In clayey soils, it improves drainage by increasing the soil’s porosity and preventing waterlogging.
Reduces Soil Erosion: Manure acts as a natural binder, preventing soil erosion caused by wind or water. The organic matter in manure helps to bind the soil particles together, creating a stable soil structure and reducing the risk of erosion.
Effects Of Fertilizers On Soil Quality
While fertilizers offer quick and targeted nutrient supplementation to the soil, their overuse can have negative consequences for soil quality and the environment.
Salt Accumulation: Chemical fertilizers contain salts that, when applied excessively, can accumulate in the soil over time. This accumulation can lead to increased soil salinity, which hampers plant growth and negatively affects soil fertility.
Microbial Imbalance: Excessive use of chemical fertilizers can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the soil. These microorganisms play a vital role in nutrient cycling and maintaining soil health. The high concentration of synthetic nutrients in fertilizers can harm beneficial soil microbes, leading to a decline in overall soil fertility.
Environmental Pollution: Chemical fertilizers have the potential to contaminate water bodies and ecosystems when not used judiciously. Runoff from fields treated with high doses of synthetic fertilizers can carry these chemicals into nearby rivers, lakes, and groundwater, contributing to water pollution.
Short-Term Benefits: Chemical fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability to plants. However, these benefits are often short-lived, as the nutrients are quickly consumed by plants and can be washed away by rainfall or irrigation. This necessitates frequent and regular application of fertilizers, which can lead to overdependence and potential soil nutrient imbalances in the long run.
Sustainability And Long-term Effects
When comparing the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility, it’s crucial to consider their long-term sustainability and effects on the environment. Both manure and fertilizers play a significant role in enhancing soil fertility, but they differ in terms of their long-term benefits and sustainability concerns.
Long-term Benefits Of Manure
Manure offers several long-term benefits for maintaining soil fertility. Firstly, it enriches the soil with essential nutrients and organic matter, promoting the growth of healthy crops and improving overall soil health. Secondly, manure increases soil water retention capacity, reducing the risk of erosion and enhancing the soil’s structure for long-term sustainability.
Sustainability Concerns With Fertilizers
While chemical fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability to plants, they also pose sustainability concerns. Chemical fertilizers can lead to the depletion of soil fertility over time, as their excessive use may disrupt the natural balance of soil microorganisms and lead to long-term soil degradation. Moreover, they can contribute to environmental pollution and affect the long-term sustainability of agricultural practices.
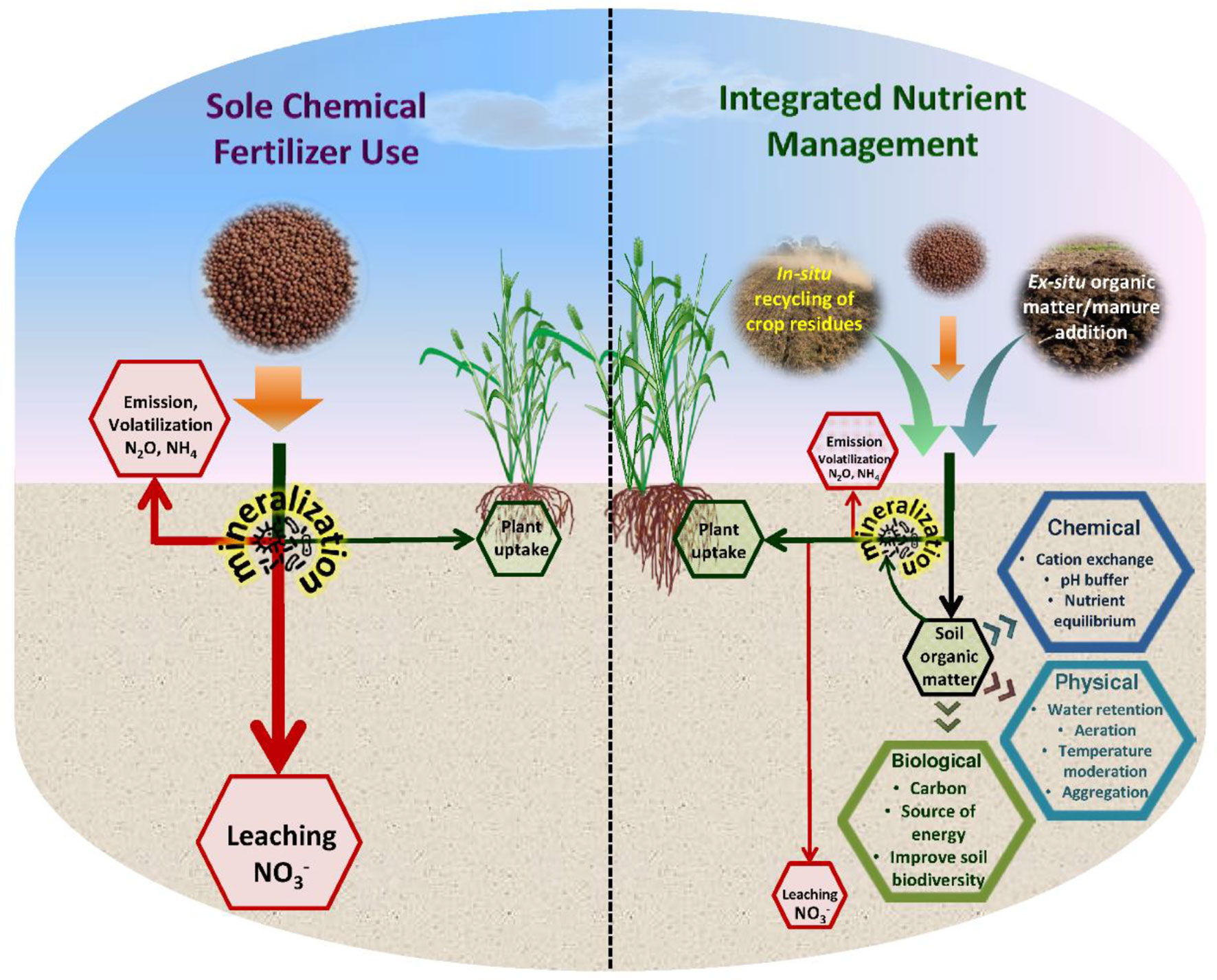
Credit: www.frontiersin.org
Cost And Accessibility
Manure enriches the soil with organic matter and nutrients, maintaining soil fertility without reducing it. However, chemical fertilizers can decrease soil fertility when used excessively, making them suitable for short-term use only.
Cost-effectiveness Of Manure
Manure is a cost-effective option for maintaining soil fertility.
Accessibility Of Fertilizers
Fertilizers are easily accessible for maintaining soil fertility.
When considering the cost-effectiveness of manure, it is important to note that it provides added nutrients to the soil, improving its quality.
On the other hand, fertilizers can be more readily available compared to manure, making them a convenient option for farmers.
| Manure | Fertilizers |
|---|---|
| Cost-effective | Generally more accessible |
| Improves soil quality | Readily available for immediate use |
- Manure enriches the soil with nutrients.
- Fertilizers may reduce soil fertility over time if overused.
- Manure is beneficial for soil quality improvement.
- Fertilizers are easily accessible but should be used judiciously.
Considering the overall cost and availability aspects, both manure and fertilizers play essential roles in maintaining soil fertility.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Use Of Manure And Fertilizers In Maintaining Soil Fertility?
Manure enriches soil nutrients and improves soil quality, while fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability. Manure promotes water retention and reduces erosion, and supports soil-friendly bacteria. Fertilizers can make soil dry, increase erosion rates, and alter soil acidity. Proper use of both enhances soil fertility.
What Is The Difference Between Manure And Fertilization Fertilizer?
Manure enriches soil nutrients and organic matter, maintaining fertility. Fertilizers, often inorganic, can reduce soil fertility with excessive use.
What Does Fertilizer Do For Soil Fertility?
Fertilizer enriches soil with essential nutrients, enhancing soil fertility and promoting healthy plant growth.
How Manure Increases The Fertility Of Soil?
Manure enriches soil with nutrients and organic matter, improving water retention and fostering soil-friendly bacteria.
Conclusion
The use of manure and fertilizers both contribute to maintaining soil fertility. Manure enriches the soil with nutrients and organic matter, enhancing water retention and reducing erosion. On the other hand, chemical fertilizers provide immediate access to specific nutrients but can also lead to decreased soil fertility and environmental harm with excessive use.
Both options have their advantages and limitations, and a balanced approach is crucial for sustainable soil management.